What are the hazards associated with operating powered industrial trucks?
What are the hazards associated with operating powered industrial trucks?
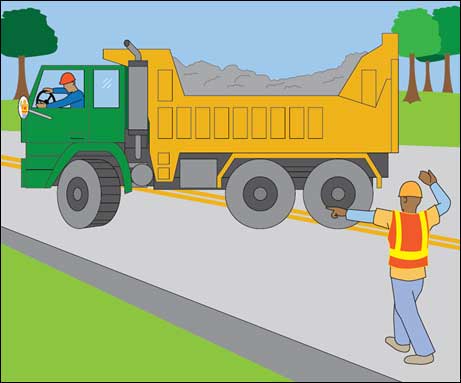
There are many types of powered industrial trucks. Each type presents different operating hazards. For example, a sit-down, counterbalanced high-lift rider truck is more likely than a motorized hand truck to be involved in a falling load accident because the sit-down rider truck can lift a load much higher than a hand truck. Workplace type and conditions are also factors in hazards commonly associated with powered industrial trucks. For example, retail establishments often face greater challenges than other worksites in maintaining pedestrian safety. Beyond that, many workers can also be injured when (1) lift trucks are inadvertently driven off loading docks; (2) lifts fall between docks and an unsecured trailer; (3) they are struck by a lift truck; or (4) they fall while on elevated pallets and tines.
What can be done to reduce the hazards related to powered industrial trucks?
Determining the best way to protect workers from injury largely depends on the type of truck operated and the worksite where it is being used. Employers must ensure that each powered industrial truck operator is competent to operate a powered industrial truck safely, as demonstrated by the successful completion of the training and evaluation specified in 29 CFR 1910.178(l)(1).