Being overweight or obese isn’t a cosmetic problem. These conditions greatly raise your risk for other health problems.
Being overweight or obese isn’t a cosmetic problem. These conditions greatly raise your risk for other health problems.
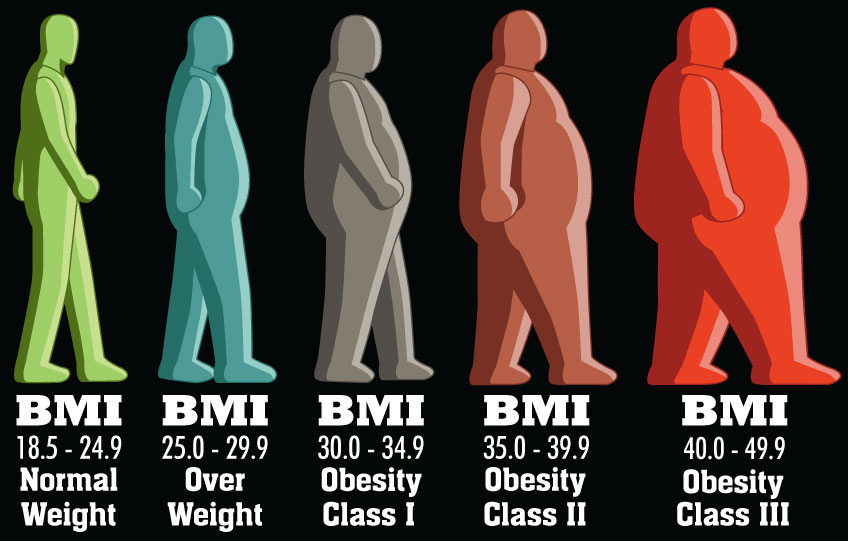
Overweight and Obesity-Related Health Problems in Adults:
- Coronary Heart Disease
- High Blood Pressure
- Stroke
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Abnormal Blood Fats
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Cancer
- Osteoarthritis
- Sleep Apnea
- Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
- Reproductive Problems
- Obesity can cause menstrual issues and infertility in women.
- Gallstones
via What Are the Health Risks of Overweight and Obesity? – NHLBI, NIH.