 There is risk in not knowing how to manage people. The Blake & Mouton’s Managerial Grid is a great tool to evaluate leadership style for change and improvement.
There is risk in not knowing how to manage people. The Blake & Mouton’s Managerial Grid is a great tool to evaluate leadership style for change and improvement.
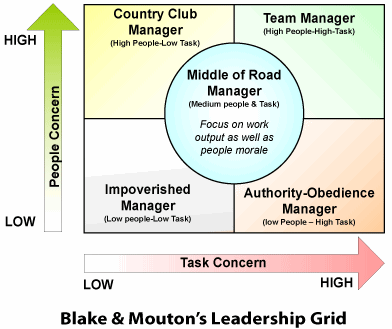
The managerial grid model (1964), developed by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton, is a behavioral leadership model. The model is an excellent way to map out different leadership styles, and an excellent way to evaluate the leadership performed by leaders and managers.
This model identifies five different leadership styles based on the concern for people and the concern for production. It is important to remember that none of the concerns are right or wrong, and the concerns are ideally balanced to the respective situational context of leadership.
Concern for People relates to the degree to which a leader considers needs of employees and team members before deciding how to accomplish a task. A high degree of concern could be coupled to a more democratic leadership style, whereas a low concern for people could be coupled to an autocratic leadership style.
Concern for Production relates to the degree to which a leader emphasizes production effectiveness and efficiency when deciding how best to accomplish tasks.
By charting the position in the grid it is possible to diagnose which leadership style is being performed, and to evaluate the appropriateness of the style of leadership.
via What is Blake & Mouton’s Managerial Grid?.
 Behaviors have always had a role in safety dating back to prehistoric times, and they always will. Behaviors were the primary, and sometimes only, tools for survival, remaining today as the last tool when all else fails. When in an environment you do not control or when you lack the right tools or systems fail, it is up to you to behave in a manner for self-preservation. This is popularized with the common statement, “You are the one responsible for your safety.” This is not ideal; it is, however, reality.
Behaviors have always had a role in safety dating back to prehistoric times, and they always will. Behaviors were the primary, and sometimes only, tools for survival, remaining today as the last tool when all else fails. When in an environment you do not control or when you lack the right tools or systems fail, it is up to you to behave in a manner for self-preservation. This is popularized with the common statement, “You are the one responsible for your safety.” This is not ideal; it is, however, reality.








