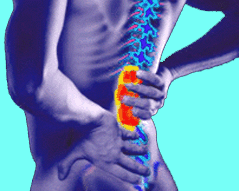
 Your back is made of bones, muscles, and other tissues extending from your neck to your pelvis. Back injuries can result from sports injuries, work around the house or in the garden, or a sudden jolt such as a car accident. The lower back is the most common site of back injuries and back pain. Common back injuries include:
Your back is made of bones, muscles, and other tissues extending from your neck to your pelvis. Back injuries can result from sports injuries, work around the house or in the garden, or a sudden jolt such as a car accident. The lower back is the most common site of back injuries and back pain. Common back injuries include:
- Sprains and strains
- Herniated disks
- Fractured vertebrae
These injuries can cause pain and limit your movement. Treatments vary but might include medicines, icing, bed rest, physical therapy, or surgery. You might be able to prevent some back injuries by maintaining a healthy weight, lifting objects with your legs, and using lower-back support when you sit.









