The HR executive has a vital role in controlling risk. A major component of Risk Management planning is risk avoidance. Many risks can be avoided by controlling and planning the human side of the corporate equation. Succession planning, adequate severance and outplacement, executive coaching and development will ensure that an organization has the means to deal with current and future challenges .
Tag: risk management
Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout)
Energy sources including electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, thermal or other sources in machines and equipment can be hazardous to workers. During the servicing and maintenance of machines and equipment, the unexpected startup or release of stored energy could cause injury to employees.
Control hazardous energy by following Lockout/Tagout procedures.
via Safety and Health Topics | Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout).
What Can Safety Learn from Lean?
 If you think lean is only for manufacturing, look it up on Wikipedia. You will find that lean principles, lean thinking and lean tools have been adapted and applied to everything from service industries to software development and now are being used to reduce the greatest waste of all: workplace injuries.
If you think lean is only for manufacturing, look it up on Wikipedia. You will find that lean principles, lean thinking and lean tools have been adapted and applied to everything from service industries to software development and now are being used to reduce the greatest waste of all: workplace injuries.
via What Can Safety Learn from Lean? | Safety content from EHS Today.
How to Prevent Needlestick and Sharps Injuries
Construction Safety and Health
 Construction workers build our roads, houses, workplaces, and repair/maintain our nations physical infrastructure. This work includes many hazardous tasks and conditions such as work at height, excavations, noise, dust, power tools and equipment, confined spaces and electricity.
Construction workers build our roads, houses, workplaces, and repair/maintain our nations physical infrastructure. This work includes many hazardous tasks and conditions such as work at height, excavations, noise, dust, power tools and equipment, confined spaces and electricity.
via CDC – Construction Safety and Health – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic.
Preventing Sexual Harassment in the Workplace
 Preventing sexual harassment in the workplace, though difficult, is critically important. Fortunately, federal and state courts that have wrestled with the complex issues present in sexual harassment litigation have identified three steps an organization should take to prevent sexual harassment as well as liability for incidents that may nevertheless occur.
Preventing sexual harassment in the workplace, though difficult, is critically important. Fortunately, federal and state courts that have wrestled with the complex issues present in sexual harassment litigation have identified three steps an organization should take to prevent sexual harassment as well as liability for incidents that may nevertheless occur.
Step 1—Develop a Written Sexual Harassment Policy and Procedures.
Step 2—Distribute the Sexual Harassment Policy.
Step 3—Educate the Workforce and Train Supervisors.
An organization that diligently takes these three steps will significantly reduce sexual harassment complaints and protect the organization from costly litigation.
via Risk Managers’ Forum—Preventing sexual harassment in the workplace 08/08.
Managing Human Capital Risk
 The potential for risk in human resources can negatively affect entire business organizations — yet only half of organizations say they have a formal plan to assess such risks. It’s up to HR leaders to better understand the risks and the potential costs they represent to the business.
The potential for risk in human resources can negatively affect entire business organizations — yet only half of organizations say they have a formal plan to assess such risks. It’s up to HR leaders to better understand the risks and the potential costs they represent to the business.
via Human Resource Executive Online – Managing Human Capital Risk.
The Most Important Step in Risk Management
Safety Committee Meeting Tips
 Health and Safety Committee meetings should be held regularly on a specific day and time and at least on a quarterly basis (i.e. the first Thursday of each month/quarter at 8:30 A.M.). New committees should consider meeting on a more frequent basis. When a meeting schedule is planned well in advance, the members are then in a better position to arrange for their attendance and prepare for discussion.
Health and Safety Committee meetings should be held regularly on a specific day and time and at least on a quarterly basis (i.e. the first Thursday of each month/quarter at 8:30 A.M.). New committees should consider meeting on a more frequent basis. When a meeting schedule is planned well in advance, the members are then in a better position to arrange for their attendance and prepare for discussion.
A typical Committee meeting should include:
- Review of unfinished items from the previous meeting(s) and/or activities.
- Status reports from any sub-committees.
- Discussion/review of safety inspection reports and the actions taken to correct observed hazards.
- Review of accident/incidents sustained since the previous meeting and a discussion of measures to prevent similar accidents and incidents.
- Review of the status of current action plans or training programs.
- Review of outstanding recommendations developed by outside loss control consultants and/or Department of Commerce health and safety compliance inspectors.
- Discussion about activities related to future action plans and/or training programs.
- Discussion about special activities such as health fairs.
- Discussion about new business, future agenda items, projects and meeting dates.
Avoid Dangerous Scaffold Accidents
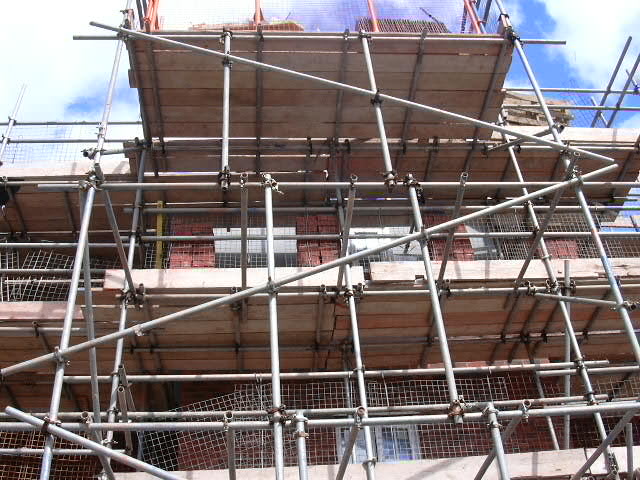 The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) reports that falls are a leading cause of traumatic death on the job. Many of these incidents involve scaffolding. Scaffolds are working platforms suspended by ropes, or other means, from an overhead structure. Falls frequently occur as the result of:
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) reports that falls are a leading cause of traumatic death on the job. Many of these incidents involve scaffolding. Scaffolds are working platforms suspended by ropes, or other means, from an overhead structure. Falls frequently occur as the result of:
* Improper installation or operation of scaffold equipment.
* Defective scaffold equipment.
* Insufficient worker safety training.
* Failure to provide or use personal fall protection equipment.
via High Risk: Despite Regulations, Scaffold Accidents Continue | Safety.com.